1940
JUNE
1940
|
Strategic Situation -
The Mediterranean region included
two other theatres of war - the oil
production regions of the
Near East, and the Red
Sea and Italian East
Africa area:
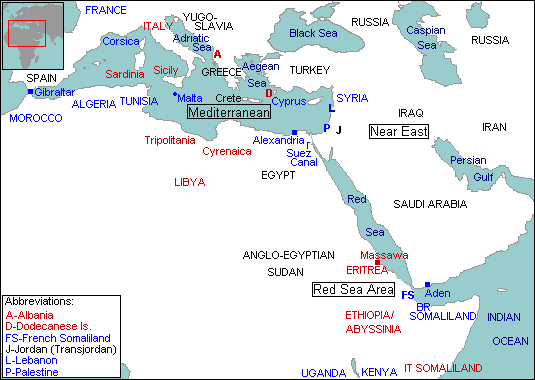
Near
East - Iraq, Persia
(Iran) and the Persian Gulf area
were within the British sphere of
influence and surrounded by Allied
or neutral countries.
Red
Sea Area – To the east Saudi
Arabia had close ties with Britain,
and at the southern end of the Red
Sea, Aden was a British colony. On
the west shore were Egypt and the
Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, and further
south French and British Somaliland.
In between the Sudan and Somaliland
were the linked Italian colonies of
Eritrea, Ethiopia (Abyssinia) and
Italian Somaliland. Bordering them
to the south was British Kenya.
Military
and Maritime Circumstances - From
bases in Italian East Africa the
Italian Air Force and Navy were
capable of cutting Allied supply
routes to Suez through the Red
Sea. The Italian army was
also powerful enough to conquer
British and French Somaliland and
posed a threat to the Sudan and
Kenya. The Italians' one major
problem was the impossibility of
supplying these forces other than by
air from Libya.
Naval
Strengths -
The
major Allied and Italian strengths
were in the Mediterranean. However
the
Italian
Navy maintained a small but useful
force in the Red Sea.
Based at Massawa were 7 destroyers,
8 submarines and 2 torpedo boats.
Against these could be deployed
ships of the East lndies Command
based at Trincomalee in Ceylon,
although these could be reinforced
through the British-controlled Suez
Canal.
|
Italy
Declared War - Italy declared war on
Britain and France on the 10th. Two weeks later
France was out of the war. Still on the 10th,
Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand and South
Africa declared war on Italy.
Red
Sea Area Operations
15th - In the
Red Sea and Indian Ocean area, four of the eight
Italian submarines based there were soon
accounted for starting with “MACALLE” which ran
aground, a total loss.
19th - At the
southern end of the Red Sea, the Italian
“GALILEO GALILEI” on patrol off Aden was
captured by armed trawler “Moonstone” following
a gun duel.
23rd - Also
in the Gulf of Aden, but off French Somaliland,
Italian boat “EVANGELISTA TORICELLI” was
sunk by destroyers “Kandahar” and “Kingston”
with sloop “Shoreham”. During the action,
destroyer “KHARTOUM” suffered an internal
explosion and sank in shallow water off Perim
Island, a total loss.
23rd -
Italian submarine “Galvani” sank Indian patrol
sloop “PATHAN” in the Indian Ocean
24th - The
following day off the Gulf of Oman, “GALVANI”
was
accounted for by sloop
“Falmouth”.
Merchant Shipping
War
- Losses in the Mediterranean throughout the war
were generally low as most Allied shipping to
and from the Middle East was diverted around the
Cape of Good Hope. To reach the Eastern
Mediterranean meant passing through the
Red Sea within reach of Italian bases
in Abyssinia.
JULY
1940
East
Africa - Italian forces from Ethiopia
occupied British border posts in Kenya and
the Sudan.
AUGUST
1940
East
Africa - Italian forces from Ethiopia
invaded British Somaliland. The capital
of Berbera was evacuated on the 14th and the
garrison carried across to Aden. Italians
entered the town five days later, just as a
British mission went into Ethiopia to
help organise uprisings against the Italians
there.
OCTOBER
1940
Red
Sea - Convoy BN7 was attacked by
Italian destroyers based at Massawa in Eritrea
on the 21st. The escorts, including New Zealand
cruiser "Leander" and the destroyer "Kimberley",
drove "NULLO" ashore with their gunfire, where
she was destroyed next day by RAF Blenheims.
1941
JANUARY
1941
East
Africa - The British and Dominion campaign
to drive out the Italians from East Africa
started. Eritrea in the north was
invaded from the Sudan by largely Indian forces,
while East African and South African troops
attacked Italian Somaliland from Kenya
to the south.
FEBRUARY
1941
East Africa -
In the north the Indian advanced into Eritrea
was
held up for
most of February and March by the Battle for
Keren. In the south, the Italian Somaliland
capital of Mogadishu was captured on the 25th,
after which British forces advanced northwest
into Ethiopia. The East lndies
Command
under Vice-Adm R. Leatham continually supported
the land campaign.
27th - After
breaking out of Massawa, Eritrea's Red Sea port,
Italian armed merchant cruiser "RAMB 1" was
located off
the Indian Ocean Maldive Islands and sunk by New
Zealand cruiser "Leander".
MARCH
1941
East
Africa - British forces were transported
from Aden to Berbera in British
Somaliland on the 16th. From there,
they advanced southwest into southern Ethiopia.
To the north, Keren fell to the attacking Indian
troops and the road was opened to the Eritrean
capital of Asmara and Red Sea port of Massawa.
APRIL
1941
Near
East
- A pro-German coup in Iraq on the
1st threatened Allied oil supplies. British and
Indian units were entering the country through
the Persian Gulf by the middle of the month. The
campaign continued through May.
East Africa - On
the Red Sea coast of Italian East Africa, the
capture of Eritrea
was completed
when Asmara was occupied on the 1st and the port
of Massawa on the 8th. Two days earlier, Addis
Ababa, capital of Ethiopia, had been
taken. Italian resistance continued mainly in
the north of the Ethiopia.
3rd - Leading up to the capture of Massawa,
the surviving eight Italian destroyers and
torpedo boats were lost or scuttled. On the 3rd,
five seaworthy destroyers sailed to attack Port
Sudan, Sudan further north along the Red Sea
shore. Shore-based Swordfish from carrier
"Eagle" sank "MANIN" and "SAURO". 8th -
Before the final scuttling at Massawa, Italian
MTB MAS-213 torpedoed and damaged cruiser
"Capetown" escorting a convoy off Massawa. Four
Italian submarines did manage to escape and
eventually reached Bordeaux, France after
sailing right round Africa.
MAY
1941
Near East -
British bases in Iraq
were
besieged as
British and Dominion forces advanced on Baghdad
from Jordan and the Persian Gulf. An armistice
was signed on the 31st May and Baghdad occupied
the next day.
East Africa -
The remaining major Italian forces in northern
Ethiopia surrendered at Amba Alagi on
the 19th. Some resistance continued until
November.
JUNE
1941
Near East -
Concerned about German influence in Vichy French
Lebanon and Syria, British,
Dominion and Free French forces invaded on the
8th from points in Palestine, Jordan and later
from Iraqi territory. The Free French entered
Damascus on the 21st, but strong resistance
continued into July. During the campaign a Royal
Navy cruiser and destroyer force, including
cruisers Australian "Perth" and New Zealand
"Leander", provided close support on the Army's
flank. They also fought a series of actions with
Vichy French warships as well as German
aircraft. A number of British destroyers were
damaged, but a French destroyer and submarine
were sunk. 16th - Fleet Air Arm
torpedo-bombers flying from Cyprus sank the
large destroyer "CHEVALIER PAUL". 25th -
Submarine "Parthian" torpedoed submarine
"SOUFFLEUR"
JULY
1941
Near
East
- An Allied/Vichy French armistice signed in the
middle of the month brought the fighting in Lebanon
and Syria to an end.
AUGUST
1941
Near East -
The possibility of a pro-Axis coup d'etat led to
Anglo-Soviet forces going into Persia (Iran)
on the 25th from points in Iraq, the Persian
Gulf and Russia. A cease-fire was announced
within four days, but later violations led to
Teheran being occupied in the middle of
September. The landings in Persia from the Gulf
were made from a small force of British,
Australian and Indian warships of the East
ladies Command.
|
Near
East & East Africa - With
the exception of small parts of
Ethiopia, the whole of the Middle
East with its vital oilfields and
pipelines together with East Africa
was now under Allied control.
|
NOVEMBER
1941
East
Africa - The last Italian forces
surrendered at Gondar in the north of Ethiopia
on the 27th. The Italian East African empire
ceased to exist.